Development of on-farm improved sugarcane-crushing technology
Sugarcane is an important cash crop, which is grown in tropical and sub-tropical regions
Sugarcane accounts for 65 % of the global sugar production
Pakistan is the 5th largest sugarcane-producing country in the world
The area of cultivation was 1.172 million hectares with an average production of about 66.5 million tonnes
Punjab accounts for 68 % of total sugarcane production
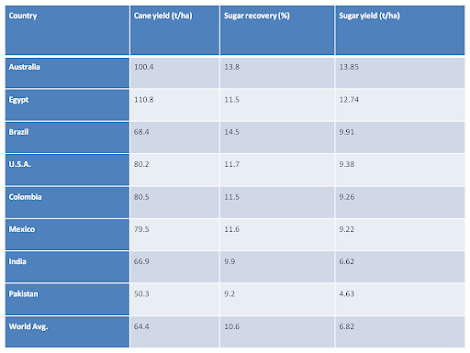
The average recovery of sugar is 10 % (the world average is 10.6 %)
The average national yield is 56.5 tonnes per hectare
The crushing capacity of 86 sugar mills is over 50 million tonnes
Recommended varieties of sugarcane
Punjab
Early maturing: BL – 4, L –116, BF – 162, CP 43-33,CP 72-2086, CP 77-400, SPSG-26, CPF-237
Mid-season: TRITON, COL –54, SPF-213
Late maturing: L –118, COJ-84
Sindh
Lower Sindh (areas south of Hyderabad)
Early maturing: BL –4
Mid season: PR –1000, BF –129
Late maturing: NIA-98
Upper Sindh (areas north of Hyderabad)
Early maturing: BL-4, L –113, L –116, TRITON, SPSG-26
Late maturing: NIA-98
KPK
Early maturing: CP 48-103, CP 51-21, CP 65-357, CPM –13, CO –1321, Mardan-93, JN 88-1, ABID-96, SPSG-26
Mid season: CP 77-400, CP 44-101, IM –61, L 62-96, Mardan-92, Bannu-1
Sugarcane products
The main product of sugarcane is white sugar
Other products, such as Gur, Shakkar, and brown sugar are produced at the farm level
More than 100 by-products are produced from bagasse, molasses, and press-mud
By-products include chipboards, hardboard, plywood, paper, ethanol, vinegar, acetic acid, organic fertilizer, poultry feed, fish feed, and many pharmaceutical products
Conventional method.
Animal-drawn sugarcane crushers are generally used for making Gur, Shakkar, and brown sugar, which have a crushing capacity of 1 to 1.5 tonnes per day
Tractor-operated sugarcane crushers have a crushing capacity of about 1 tonnes/h
The average juice recovery by both types of crushers is between 46 to52% depending on the variety
Unrecoverable juice is about 20-22 %
Juice recovery is significantly low as compared with sugar mills (about 70 %)
Unrecoverable juice by sugar mills is about 10 %
Issues
Transportation of sugarcane to mills is a big problem for farmers
Increased road hazards during peak season
Delayed acceptance of sugarcane by mills causes juice losses
Unattractive prices of sugarcane by mills during peak season
Conventional crushers have low crushing capacity and more juice losses
Improved sugarcane crushers at the farm level can serve as an intermediate solution
Yield sugar recovery in main sugarcane-growing countries of the world
Pests of sugarcane can vary depending on the region, but some common pests worldwide include:
Sugarcane Borers: These include top borer (Scirpophaga excerptalis), stem borers (Chilo spp., Eldana saccharina), and root borers (Emmalocera spp., Dorysthenes spp.). They bore into different parts of the sugarcane plant, causing damage and reducing yield.
Sugarcane Aphids: Aphids such as the sugarcane aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) feed on sugarcane sap, causing stunted growth and reducing sugar content.
Sugarcane Whiteflies: Whiteflies (Aleurolobus barodensis) feed on sugarcane sap and can transmit viruses, leading to yield loss and reduced sugar content.
Sugarcane Leafhoppers: Leafhoppers (Cicadellidae family) feed on sugarcane leaves, causing leaf damage and transmitting diseases.
Sugarcane Termites: Termites (Microtermes spp., Odontotermes spp.) can damage sugarcane roots and stems, leading to weakened plants and reduced yield.
Sugarcane Mealybugs: Mealybugs (Saccharicoccus sacchari) feed on sugarcane sap, causing stunted growth and reducing sugar content.
Sugarcane Scale Insects: Scale insects (e.g., Aulacaspis tegalensis) can infest sugarcane, affecting plant growth and reducing yield.
Sugarcane Mites: Mites (e.g., Oligonychus sacchari) can damage sugarcane leaves, leading to reduced photosynthesis and yield loss.
These pests can cause significant damage to sugarcane crops, leading to yield losses and reduced sugar quality if not managed effectively through integrated pest management strategies. for more







.jpg)

.jpg)

Thank you sharing Informative blog NACL Industries Ltd. in India offers various agricultural fertilizers designed to enhance farming productivity. For more information, feel free to contact us. We are committed to supporting sustainable and efficient farming practices!
ReplyDeletePesticides
Agrochemicals
Plant Growth Regulators